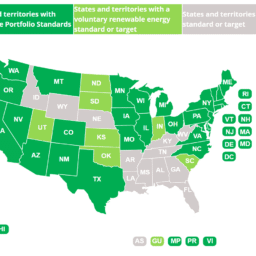
Performance based incentives (PBI), investment tax credits, and other incentives allow the solar industry to grow with a variety of solar financing options. In California, the presence of various PBIs allow for the state to reach its solar installation goals. In particular, the California Solar Initiative (CSI) program has had an incredible impact on the increase in solar installations across the state.
Understanding the California Solar Initiative
The California Solar Initiative program began in 2007 with the mission to transform the solar energy market by reducing the cost of generating solar power in addition to facilitating a self-sustaining solar industry. In order to transform the industry, the CSI set out to achieve a goal of installing 1,940 megawatts (MW) of solar capacity by the end of 2016.
The CSI Program focuses exclusively on solar energy systems used by customers who want to offset some or all of their own energy consumption. The electric portion of the CSI Program has a 10-year budget of $2.2 billion. The CSI Program pays solar consumers an incentive based on system performance. The incentives are either an upfront lump-sum payment based on expected performance, or a monthly payment based on actual performance over five years.
The golden state holds true to its name
According to the California Solar Initiative Annual Program Assessment, through the end of the first quarter of 2013, California had an estimated 1,629 MW of installed solar capacity at 167,878 customer sites. Out of all the states in the US, California represents 40 percent of the industry’s total solar capacity. The CSI Program as a whole has installed 66 percent of its total program goal, with another 19 percent of the goal reserved in pending projects.